(Ubuntu: Lesson 0)
{ Installing Ubuntu Desktop 12.04 LTS - Disable VMWare Easy Install }
| Section 0. Background Information |
- What is Ubuntu?
- Ubuntu is a computer operating system based on the Debian Linux distribution and distributed as free and open source software, using its own desktop environment. It is named after the Southern African philosophy of ubuntu ("humanity towards others")
- Most coverage of Ubuntu focuses on its use on desktop personal computers but it is also used on servers and for cloud computing.
- Ubuntu is sponsored by the UK-based company Canonical Ltd., owned by South African entrepreneur Mark Shuttleworth.
| Section 1. Prerequisite |
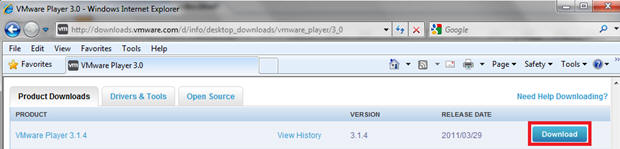
- Download VMware Player
- Instructions
- On any Window's machine, download VMware Player, if you have not already done so.
- http://downloads.vmware.com/d/info/desktop_downloads/vmware_player/3_0
- Instructions
- Download Ubuntu 12.04
- Instructions
- http://releases.ubuntu.com/12.04/
- Click on ubuntu-12.04-desktop-i386.iso
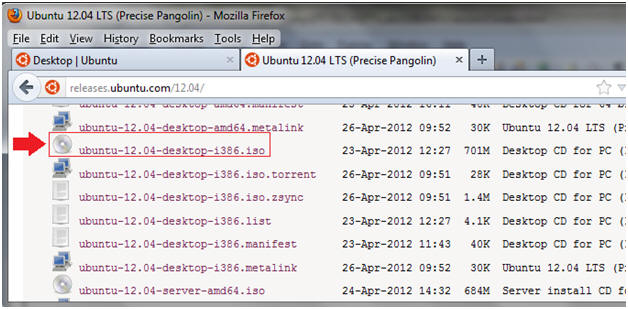
- Instructions
- Save the iso
- Instructions
- Save To C:\ubuntu-iso\ or USB:\ubuntu-iso\
- In my case, I am saving the iso to an external hard-drive, hence the (D:)
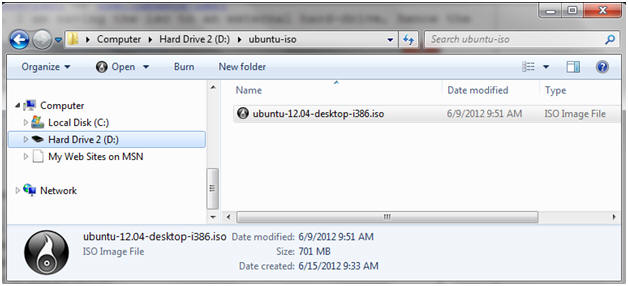
- Instructions
| Section 2. Create a New Virtual Machine |
- Open VMware Player on your windows machine.
- Create a New Virtual Machine
- Instructions
- Once VMware Player opens, Click on home, then click on create a new virtual machine.
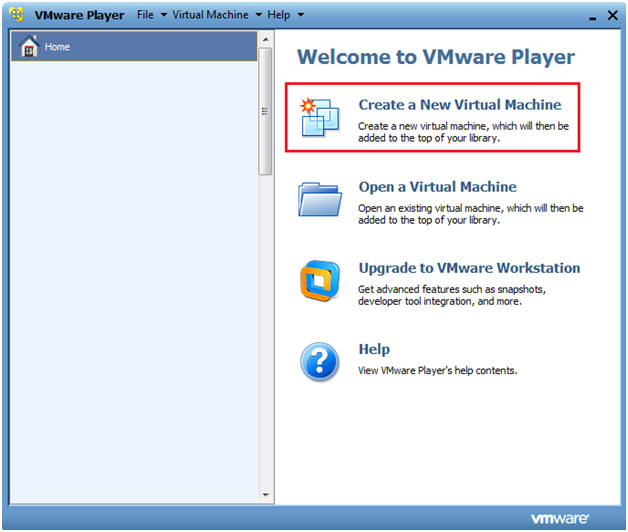
- Instructions
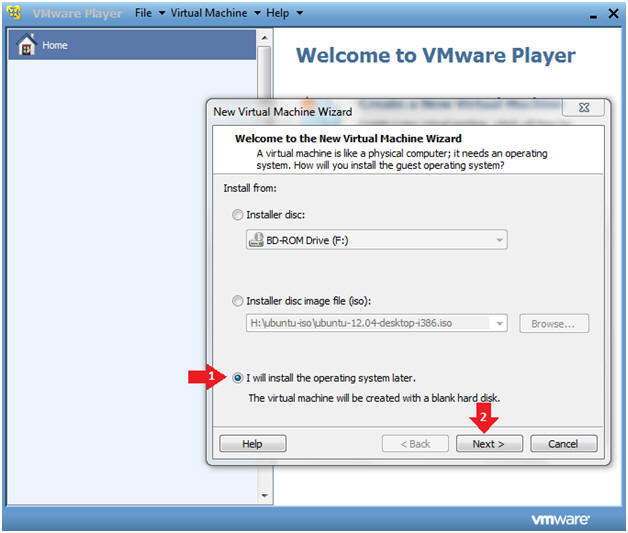
- Install Operating System Later.
- Instructions
- Select the "I will install the operating system later." radio button.
- Click Next.
- Instructions
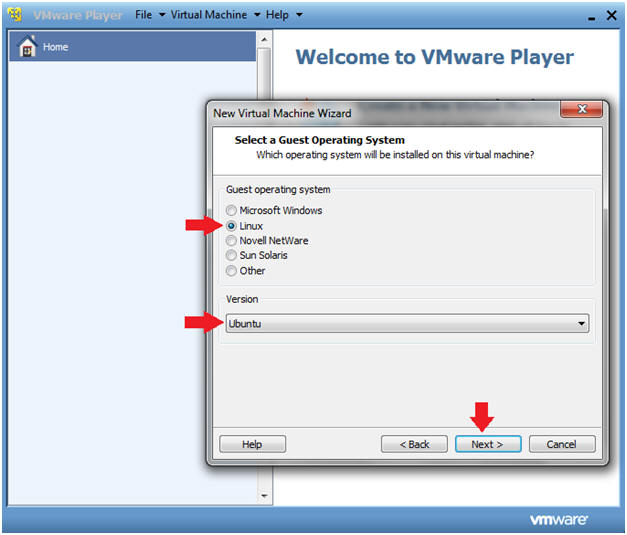
- New Virtual Machine Wizard
- Instructions
- Guest operating system: Linux
- Version: Ubuntu
- Click Next
- Instructions
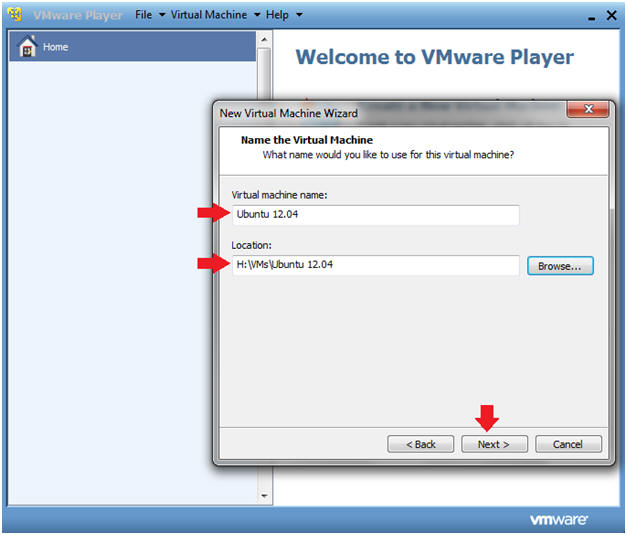
- Virtual machine Name
- Instructions
- Virtual machine name: Ubuntu 12.04
- Location: USB:\Ubuntu
12.04
- In my case, the USB letter is D:
- Instructions
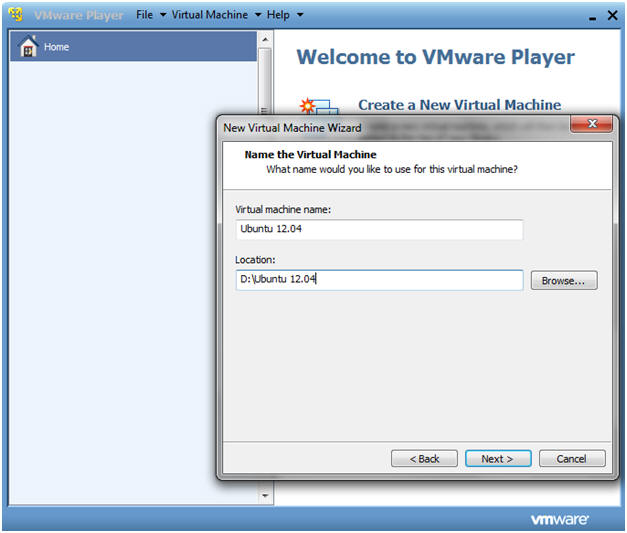
- Virtual machine Name
- Instructions
- Virtual machine name: Ubuntu 12.04
- Location: USB:\Ubuntu
12.04
- In my case, the USB letter is D:
- Instructions
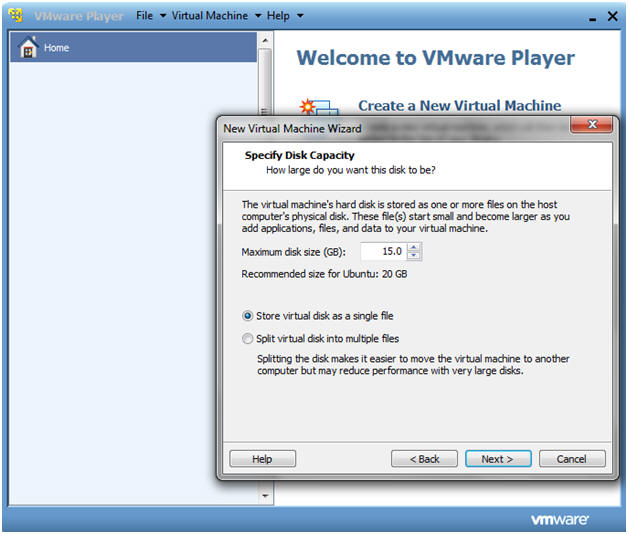
- Specify Disk Capacity
- Instructions
- Maximum disk size (GB): 15.0
- Select radio button --> Store virtual disk as a single file
- Click the Next button
- Instructions
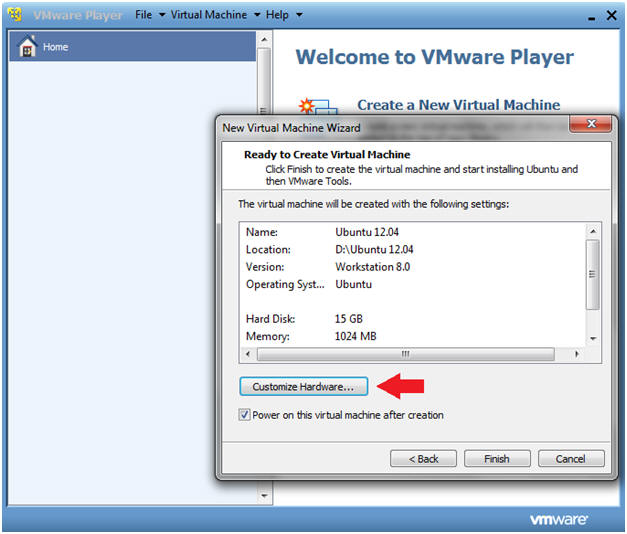
- Customize Hardware
- Instructions
- Click on the Customize Hardware button
- Instructions
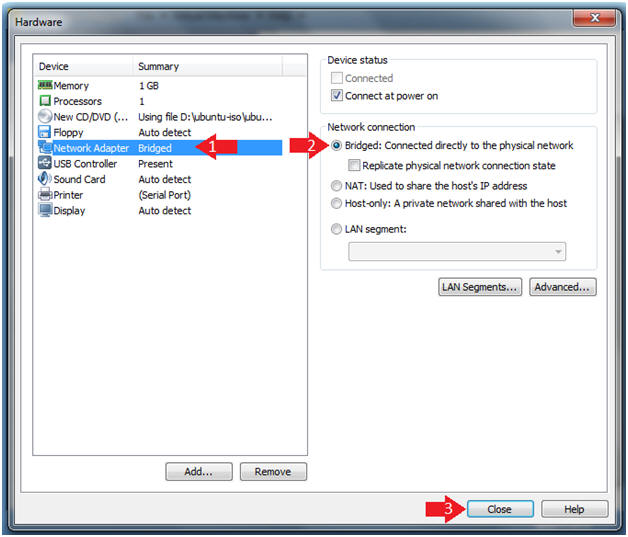
- Configure Network Adapter
- Instructions
- Click on Network Adapter
- Click on the Bridged Radio Button
- Click on the Close Button
- Instructions
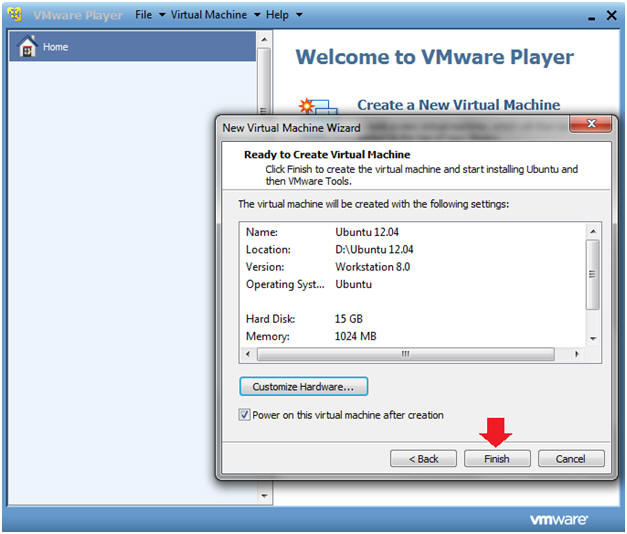
- Finish Customization
- Instructions
- Click the Finish Button
- Instructions
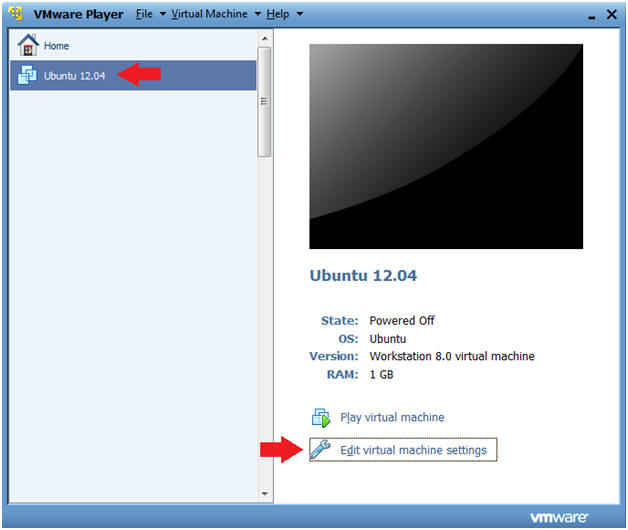
- Edit VM
- Instructions
- Click on Edit Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions
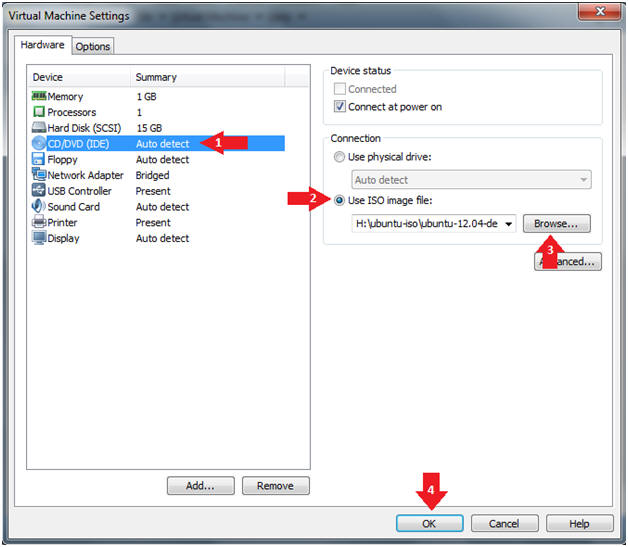
- Edit Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions
- Click CD/DVD (IDE)
- Select the "Use image file:" radio button
- Select the Browse button and navigate to ubuntu-12.04-desktop-i386.iso
- Select the OK button
- Instructions
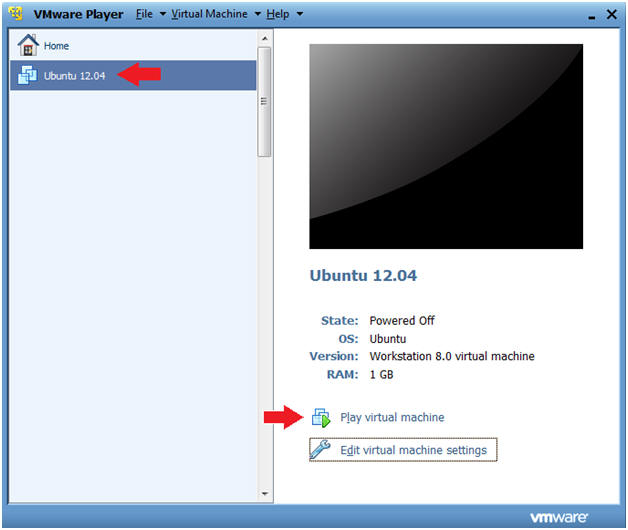
- Play VM
- Instructions
- Click on play Virtual Machine
- Instructions
| Section 3. Ubuntu 12.04 Installation |
- ISOLINUX Screen
- Informational Only
- This is the first screen before the installation starts.
- Nothing is required from you.
- Continue to next step.
- Informational Only
- Ubuntu 12.04 Screen
- Informational Only
- This is the second screen you will see.
- Nothing is required from you.
- Continue to next step.
- Informational Only
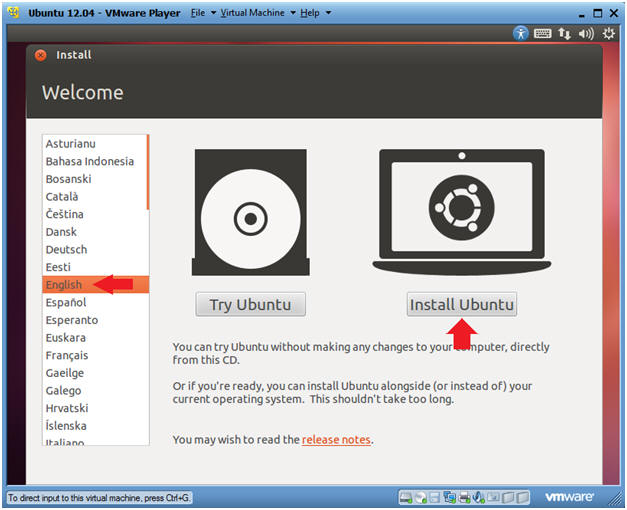
- Welcome Screen
- Instructions
- Select English
- Select Install Ubuntu
- Instructions
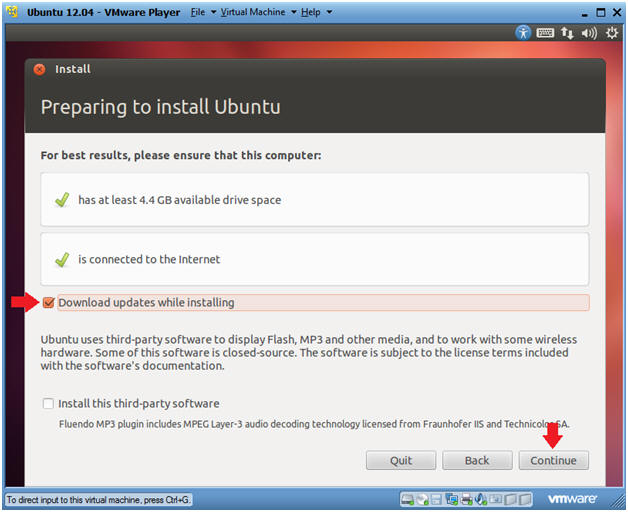
- Preparing to install Ubuntu
- Instructions
- Click the "Download updates while installing" checkbox
- Click the Continue button.
- Instructions
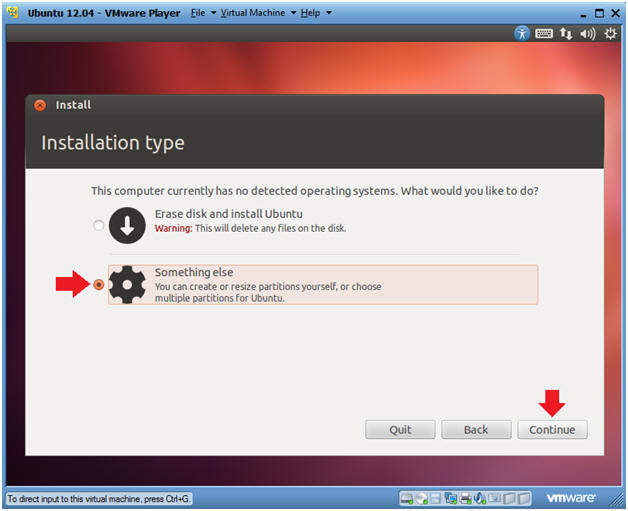
- Installation type
- Instructions
- Click the "Something else" radio button
- Click the Continue button
- Instructions
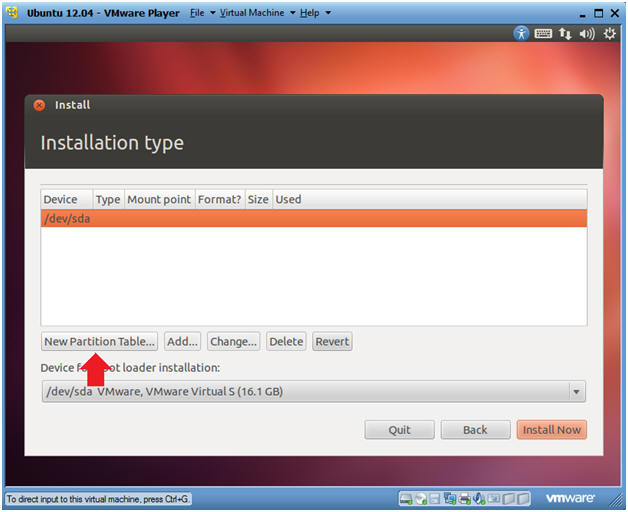
- Installation type
- Instructions
- Click the New Partition Table...
- Instructions
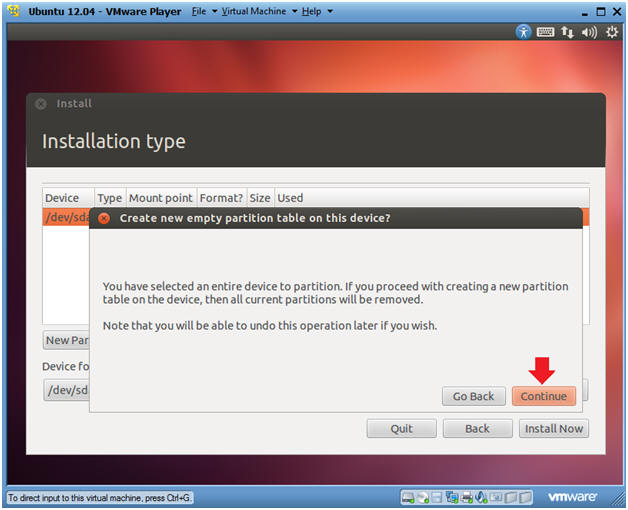
- Create new empty partition table on this
device?
- Instructions
- Click Continue.
- Instructions
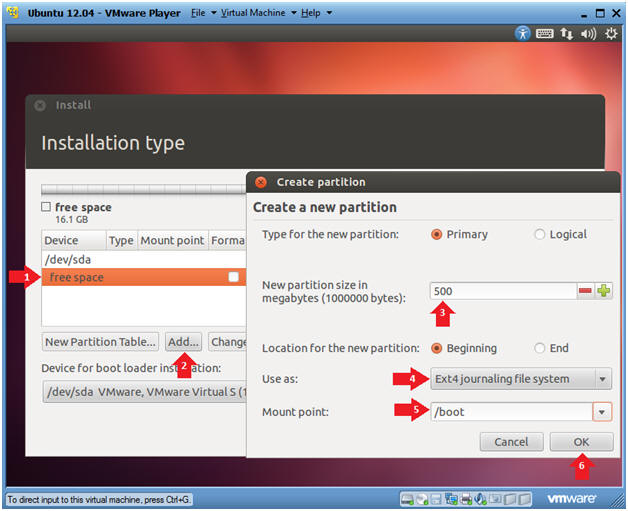
- Create the /boot file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 500
- Use as: Ext4 journaling file system
- You can also select ext2, if you do not think your /boot file system will change. For class purposes use ext4.
- Mount point: /boot
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- The /boot partition holds the kernel and other data the system needs when it boots; it cannot be under the control of LVM.
- Instructions
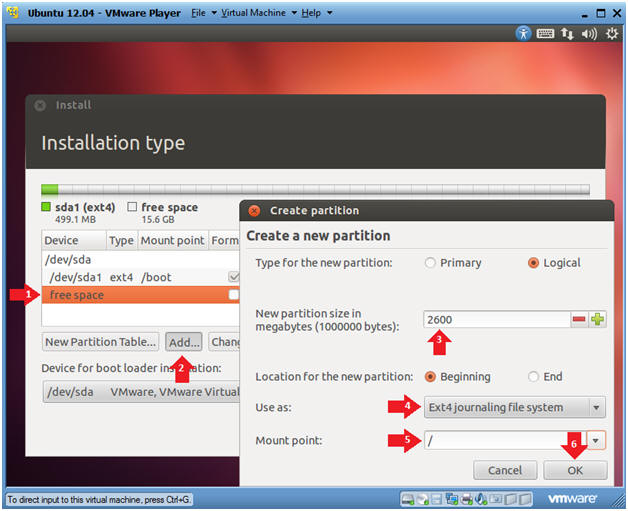
- Create the / file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 2600
- Use as: Ext4 journaling file system
- Mount point: /
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- Any file systems that are not created as a separate partition will become automatically part of the root(/) filesystem.
- Instructions
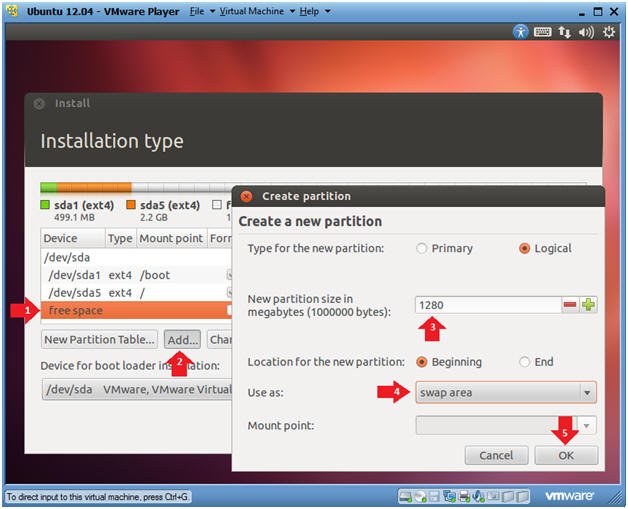
- Create the swap file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 1280
- Use as: swap area
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- Linux temporarily stores programs and data on a swap partition when it does not have enough RAM to hold all the information during processing. Also, swap is used when the system goes into hibernate mode.
- Instructions
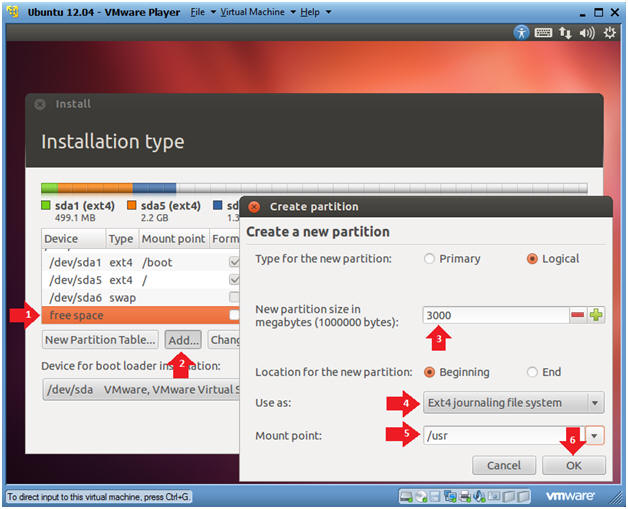
- Create the /usr file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 3000
- Use as: Ext4 journaling file system
- Mount point: /usr
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- The size of /usr depends on the number of software packages you install.
- Instructions
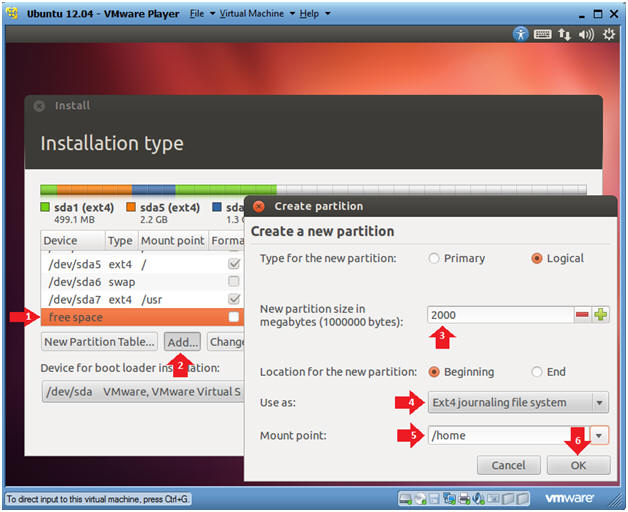
- Create the /home file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 2000
- Use as: Ext4 journaling file system
- Mount point: /home
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- Size depends on the number of users on the machine and the type of work they do.
- Instructions
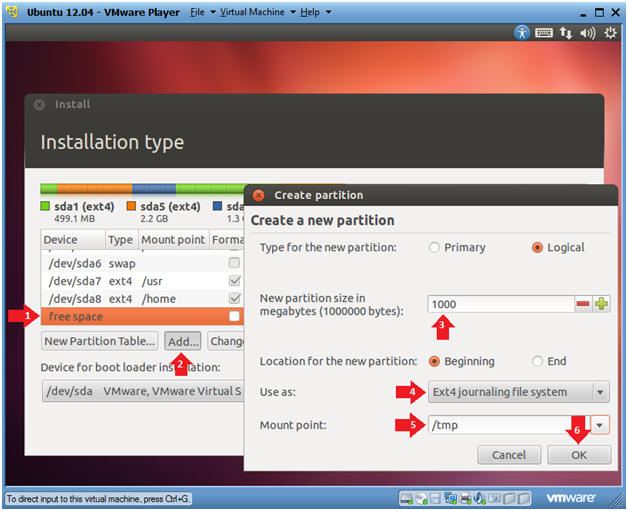
- Create the /tmp file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 1000
- Use as: Ext4 journaling file system
- Mount point: /tmp
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- Temporary files such as *.pid files reside here. For most Linux and Unix operating systems, data is not preserved between reboots.
- Instructions
- Create the /var file system
- Instructions
- Click on free space
- Click on the Add... button
- New partition size: 3000
- Use as: Ext4 journaling file system
- Mount point: /var
- Click the OK button
- Note:
- /var is short for variable. Data in this partition changes frequently.
- /var/log - Where the system log messages are stored.
- /var/mail - Where mail is stored
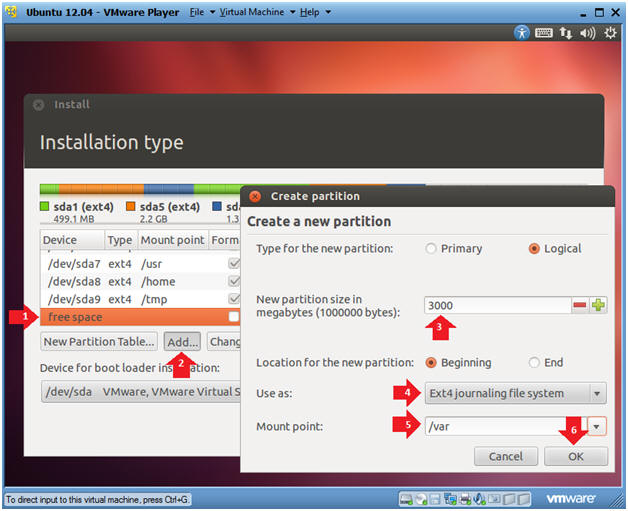
- Instructions
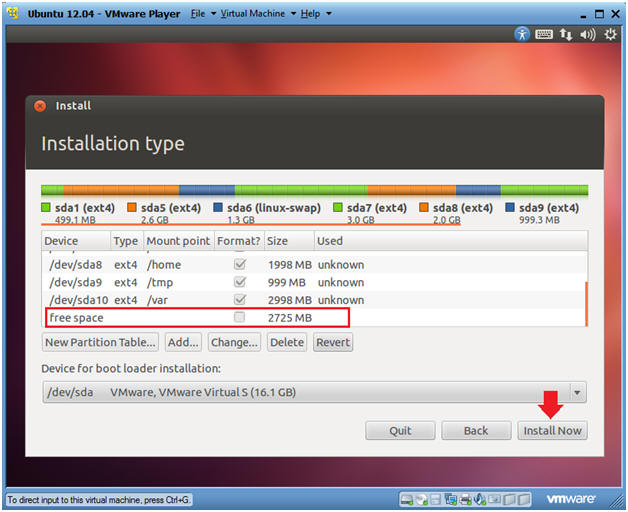
- Install Now
- Note
- Notice there is 2725 MB left in free space.
- This is on purpose and will be used later to expand files systems.
- Instructions
- Click the Install Now Button
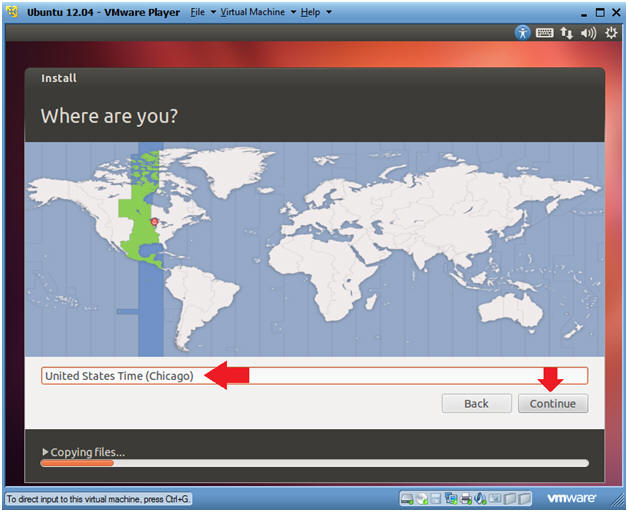
- Note
- Where are you?
- Instructions
- Select Time Zone
- Click Continue
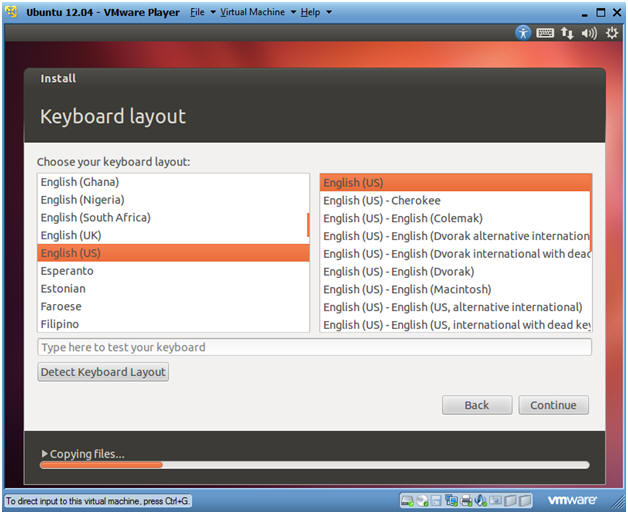
- Instructions
- Keyboard layout
- Instructions
- Choose your keyboard layout: English
- Click Continue
- Instructions
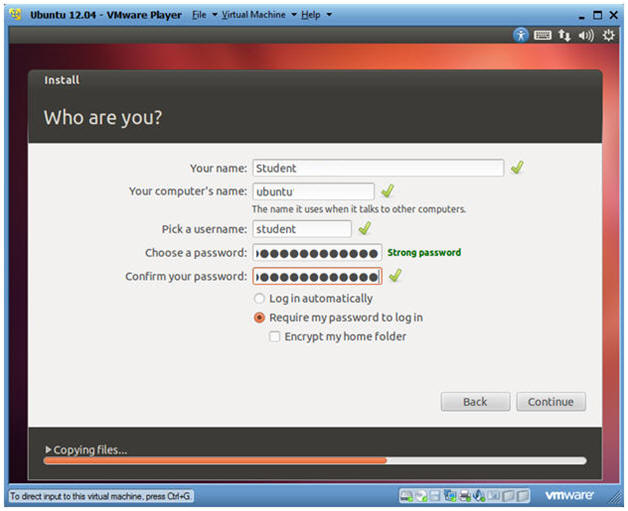
- Who are you?
- Instructions
- Your name: Student
- Your computer's name: ubuntu
- Pick a username: student
- Choose a password:
- At least 8 characters
- Alpha-Numeric
- Uppercase and Lowercase
- Symbols (!@#$%^&*, etc)
- Require my password to log in
- Click Continue
- Instructions
- Actual Installations
- Instructions
- This installation will take between 10 and 30 minutes depending on your machine resources.
- Instructions
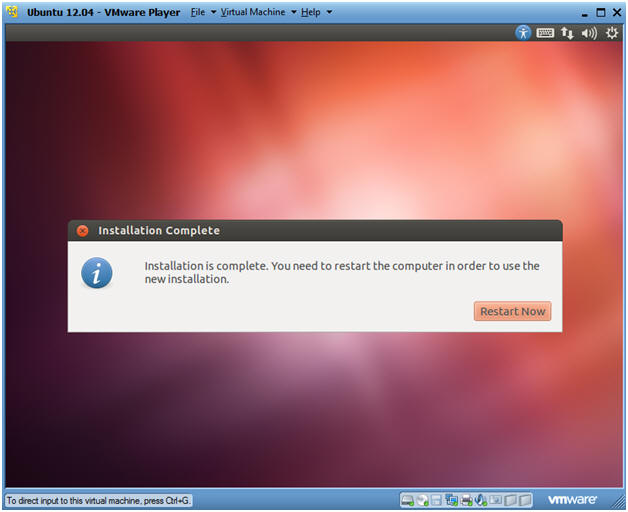
- Installation Complete
- Instructions
- Click Restart Now
- Instructions
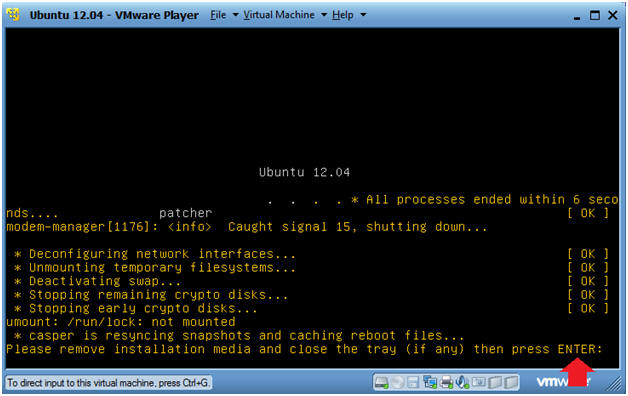
- Please remove installation media
- Instructions
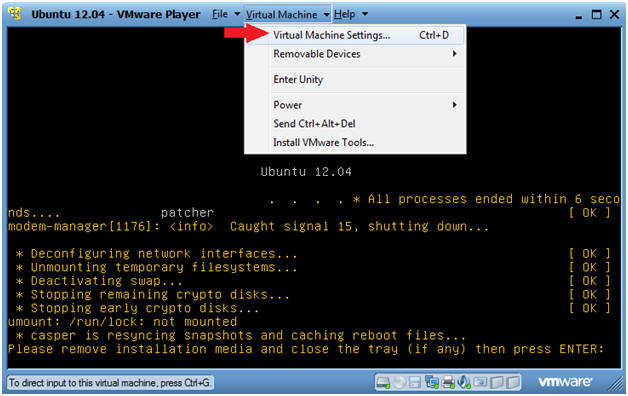
- Virtual Machine --> Virtual Machine Settings...
- Instructions
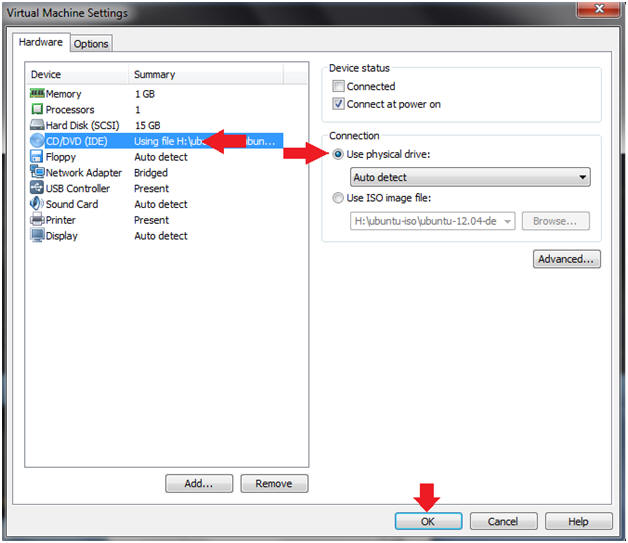
- Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions
- Select CD/DVD (IDE)
- Select Use physical drive: Auto detect
- Click OK
- Instructions
- Press Enter
- Instructions
- Press Enter
- Instructions
| Section 4. Initial Login |
- Logging in for the first time
- Instructions
- Type in the password you created in (Section 3, Step 18)
- Press <Enter>
- Instructions
| Section 5. Start Up Terminal Window |
- Ubuntu Dash
- Instructions
- Click on the Ubuntu Dash
- Instructions
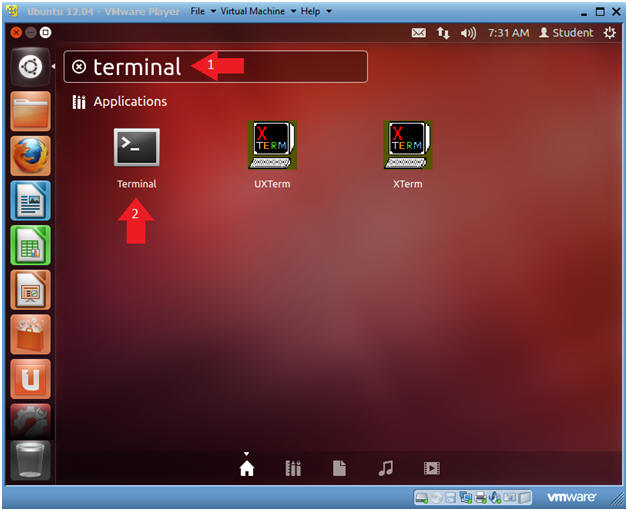
- Terminal Windows Search
- Instructions
- Type "terminal" in the search box.
- Click on the terminal.
- Instructions
| Section 6. Becoming the root user |
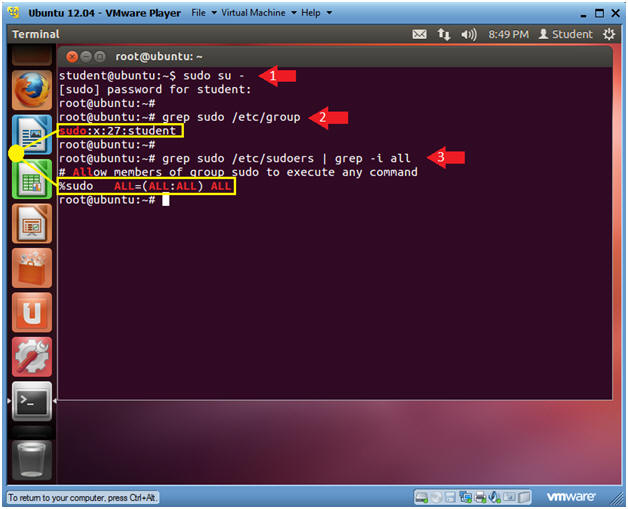
- Becoming Root
- Instructions
- sudo su -
- Note: Enter your student password.
- grep sudo /etc/group
- Note: By default, the initial user created will be added to the sudo group.
- grep sudo /etc/sudoers | grep -i all
- Note: By default, the sudo group in the sudoers file can issue any command on the system. For this reason, the student user can become root.
- sudo su -
- Instructions
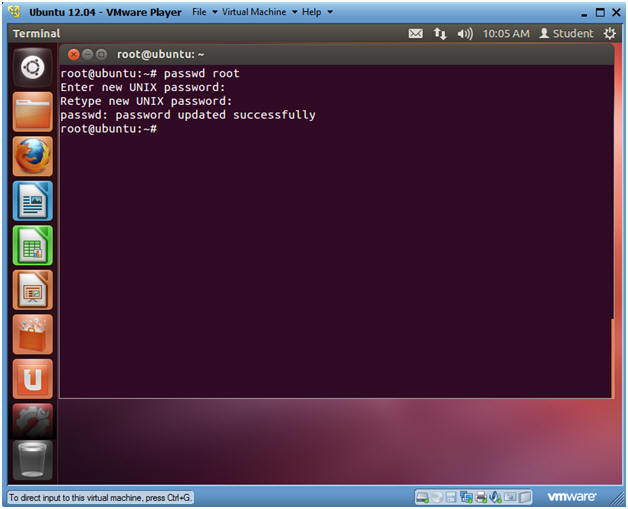
- Changing the Root Password
- Instructions
- passwd root
- Enter a new root password
- Re-Enter the new root password
- Instructions
| Section 7. Install Gnome Classic |
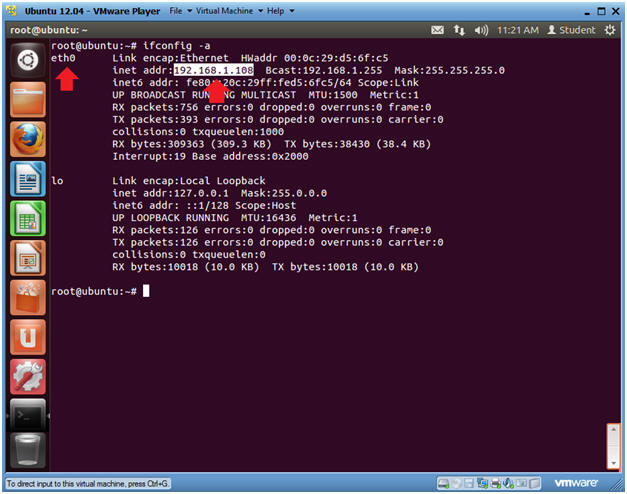
- Determine IP Address
- Instructions:
- Become the root user if you are already (See Section 6, Step 1)
- ifconfig -a
- Notes:
- eth0 is the name of my interface
- 192.168.1.108 if my IP Address
- Instructions:
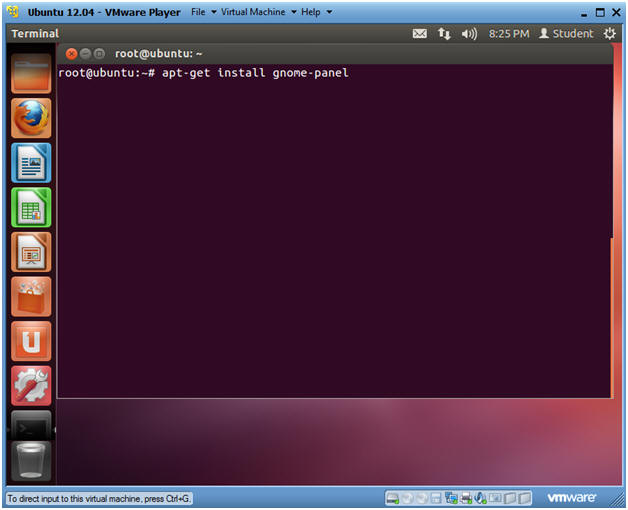
- Install the Gnome Classic Interface
- Instructions:
- apt-get install gnome-panel
- Instructions:
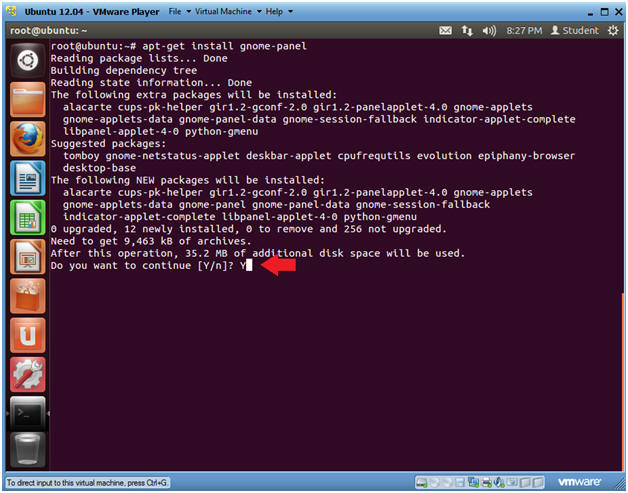
- Install the Gnome Classic Interface (Step 2)
- Instructions:
- Do you want to continue [Y/n]? Y
- Instructions:
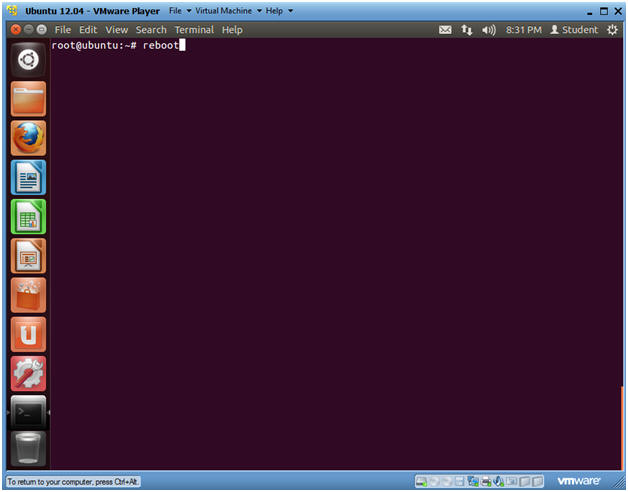
- Reboot Machine
- Instructions:
- reboot
- Instructions:
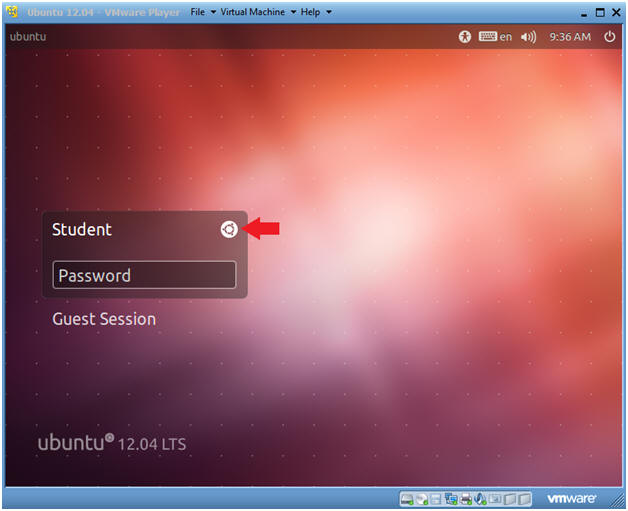
- Change to Gnome Classic
- Instructions:
- Click on the Circle
- Instructions:
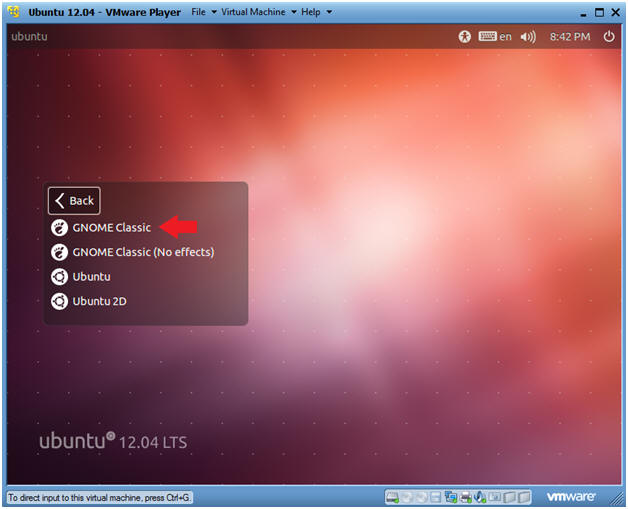
- Select Gnome Classic
- Instructions:
- Double Click on GNOME Classic
- Instructions:
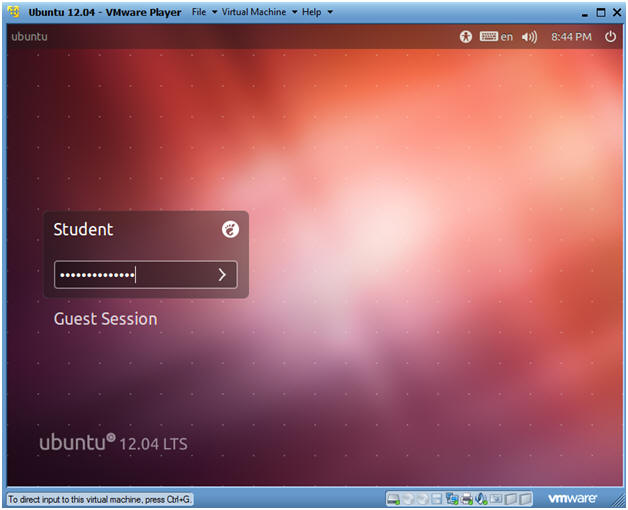
- Login to Gnome Classic
- Instructions:
- Provide the student password you created in (Section 3, Step 18).
- Instructions:
| Section 8. Basic Gnome Classic Configuration |
- Place Terminal on Top Panel
- Notes:
- In this step, we are going to drag the terminal window to the top panel.
- Instructions:
- Go to Applications --> Accessories --> Terminal
- Hold down on the Left Mouse Button when clicking on the Terminal
- Drag the Terminal to Top Panel
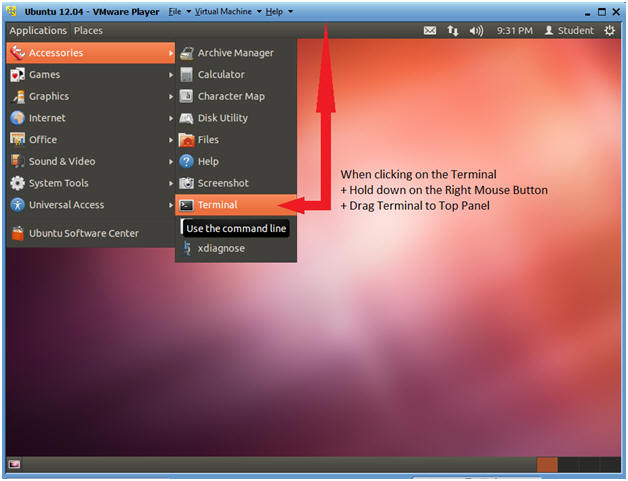
- Notes:
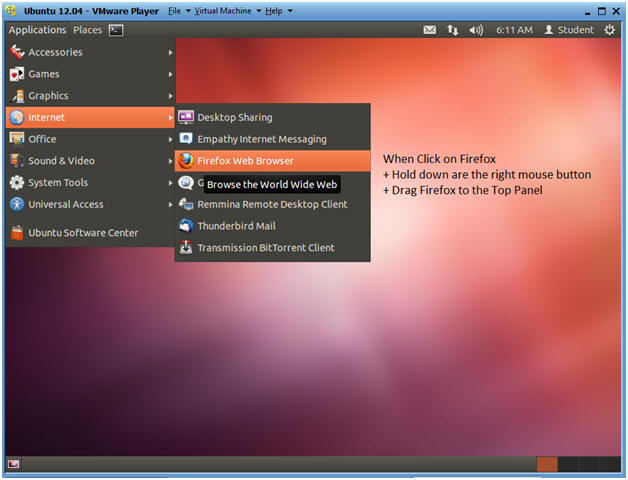
- Place Firefox on Top Panel
- Notes:
- In this step, we are going to drag the Firefox to the top panel.
- Instructions:
- Go to Applications --> Internet --> Firefox Web Browser
- Hold down on the Left Mouse Button when clicking on Firefox
- Drag Firefox to Top Panel
- Notes:
| Section 9. Configuring Date and Time |
- Go to System Settings
- Instructions:
- Applications --> System Tools --> System Settings
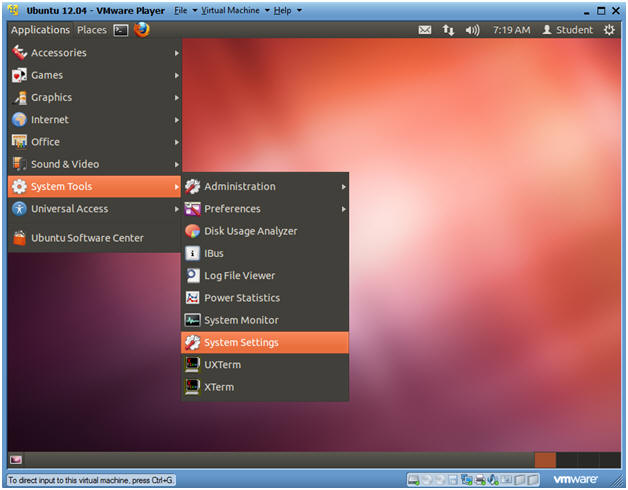
- Instructions:
- Date and Time
- Instructions:
- Click on Date and Time
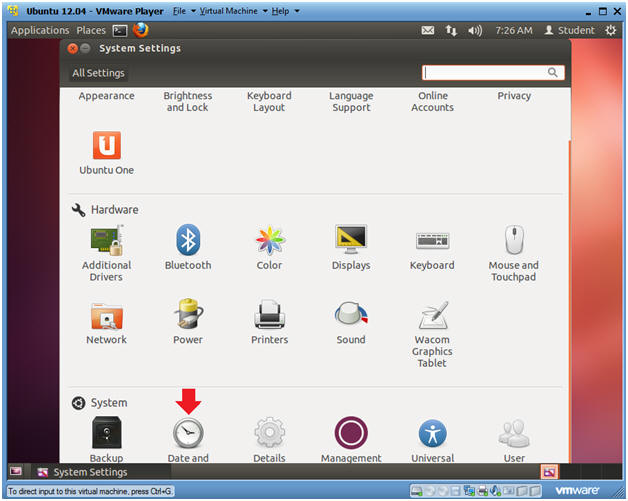
- Instructions:
- Change Date and Time
- Instructions:
- Region: Set to your Region, in my case, America.
- City: Set to a city in your Timezone, in my case, I am in the central time zone.
- Network Time: Make sure ON is selected.
- By selecting ON, both your time and date will automatically be sync'ed toward your timezone.
- Click on the X to close
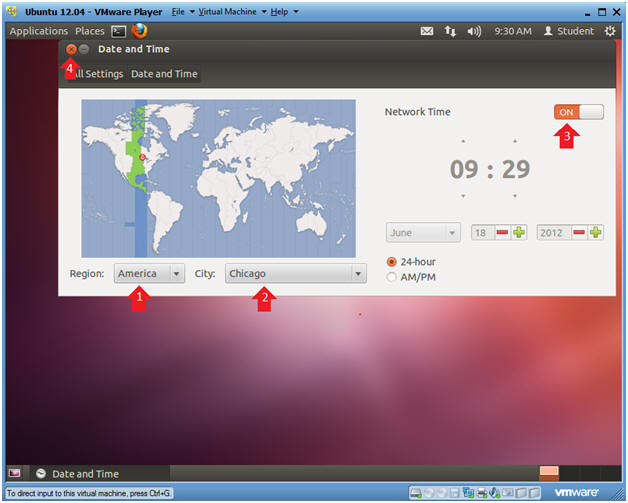
- Instructions:
| Section 10. Post VMware Configuration |
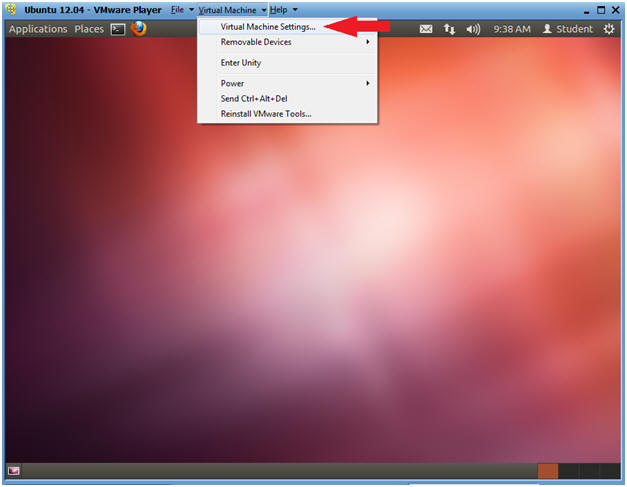
- Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions:
- Virtual Machine --> Virtual Machine Settings...
- Instructions:
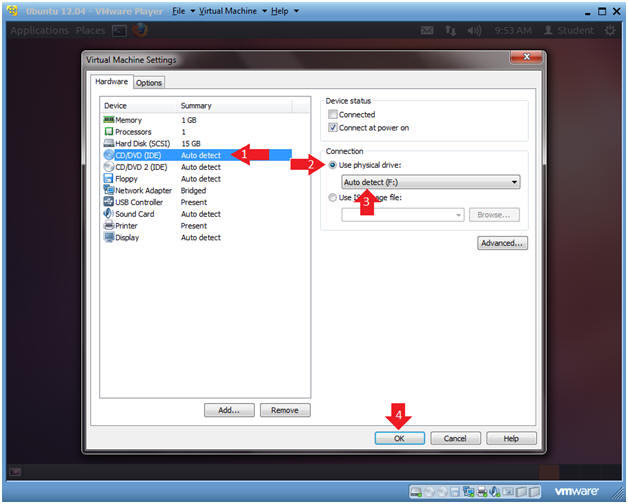
- Edit CD/DVD (IDE)
- Instructions:
- Select CD/DVD (IDE)
- Select the radio button "Use physical drive:"
- Make sure Auto Detect is selected from the down drop box.
- If #2 and #3 were NOT already set, Click OK. If #2 and #3 WERE already set, Click Cancel.
- Instructions:
| Section 11. Install VMware Tools |
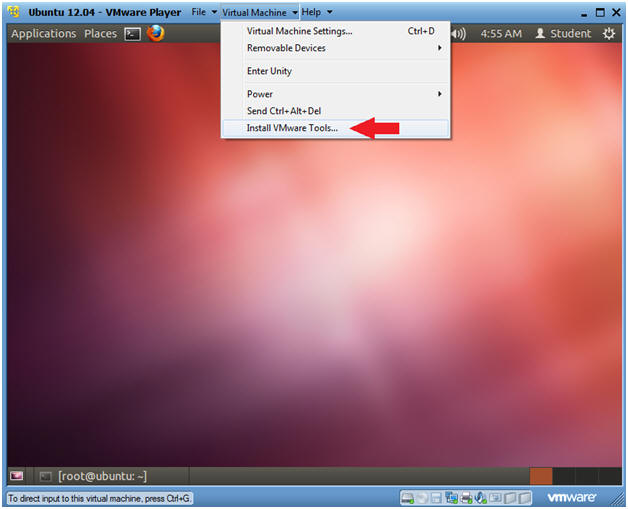
- Install VMware Tools
- Instructions:
- Virtual Machine --> Install VMware Tools...
- Instructions:
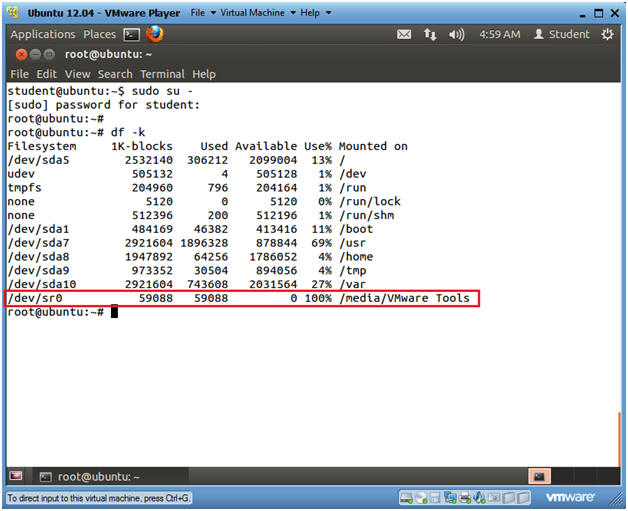
- Become Root
- Instructions:
- sudo su -
- This is not necessary if you are already root.
- df -k
- Notice the new file system called /media/VMware Tools
- sudo su -
- Instructions:
- Unzip VWware Tools
- Instructions:
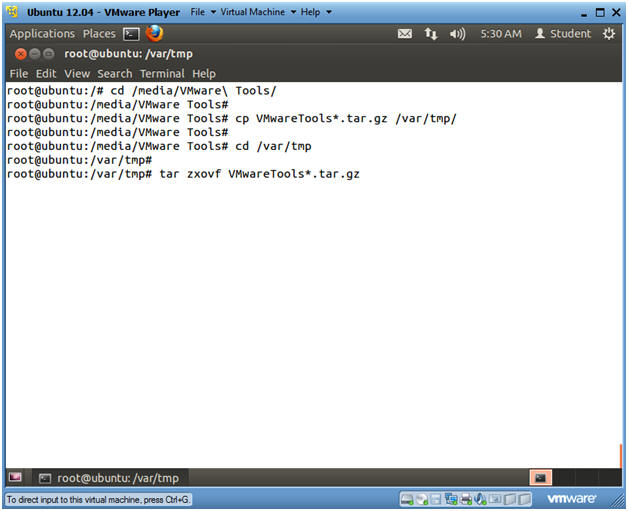
- cd /media/VMware\ Tools/
- cp VMwareTools*.tar.gz /var/tmp/
- cd /var/tmp
- tar zxovf VMwareTools*.tar.gz
- Instructions:
- Execute the vmware-install.pl
- Instructions:
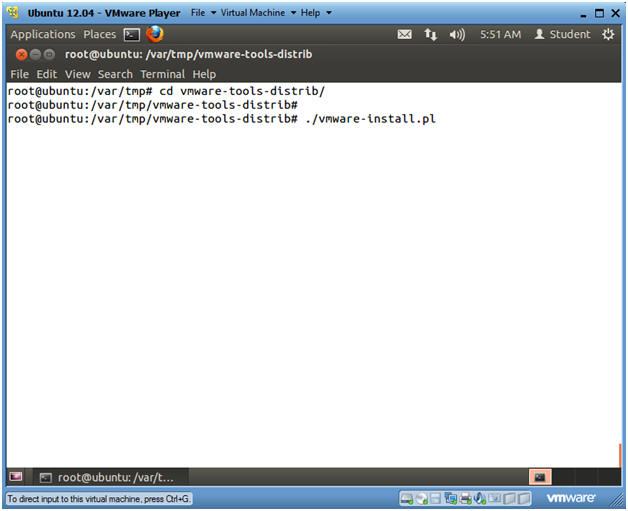
- cd vmware-tools-distrib/
- ./vmware-install.pl
- Accept all the default answer by pressing Enter for every question.
- Instructions:
| Section 12. Proof of Lab |
- Start up a Terminal Windows
- Instructions:
- Click on the Terminal Window
- OR
- Applications --> Accessories --> Terminal
- Click on the Terminal Window
- Instructions:
- Proof of Lab
-
Proof of Lab
Instructions
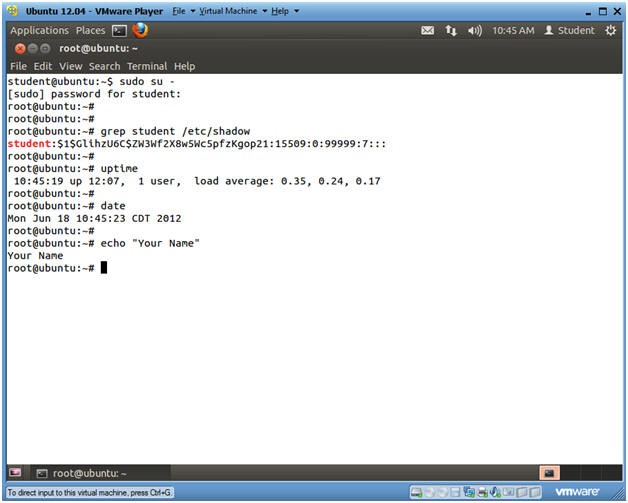
- su - root, if you are not already root.
- grep student /etc/shadow
- uptime
- date
- echo "Your Name"
- Replace the string "Your Name" with your actual name.
- e.g., echo "John Gray"
- Do a <PrtScn>
- Paste into a word document
- Upload to Moodle
-
Proof of Lab
Instructions